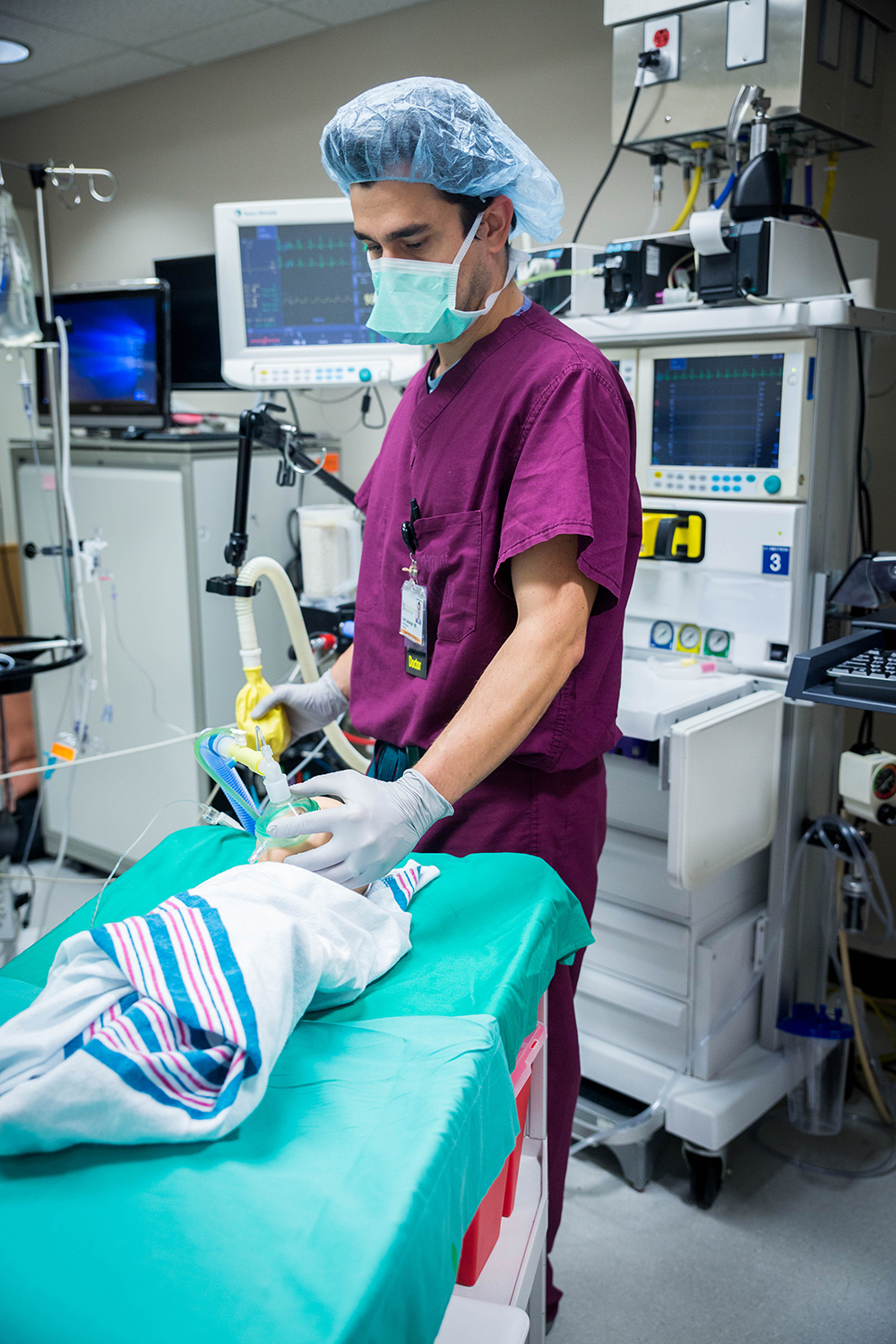
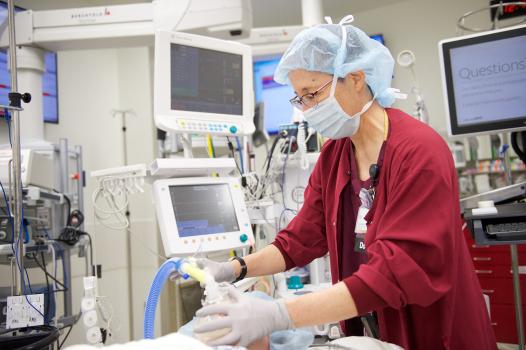
Can you describe a typical OR day for your residents?
On Monday and Wednesday through Friday, patients are expected to be in the OR at 7:30am. On Tuesdays, the in-room time is 8:30am to allow time for morning meetings and conferences beforehand. Residents typically arrive between 6 and 6:30am to set up their rooms and to perform regional blocks, etc. before moving their patients into the OR.
Residents typically get breaks in the morning and afternoon, and a longer break for lunch. Our ORs usually begin to wind down between 4 and 6pm. For any residents still in the OR at 6pm, relief is generally provided by the night-call team, late-day CRNAs, and evening shift (3-11pm) residents.
Although we follow ACGME duty hour rules, residents are expected to remain with critically ill patients or major cases as long as necessary (for patient safety or educational value). The ORs are particularly busy during the summer, but we do our best to relieve non-call providers. If residents need to leave (for personal reasons) at some earlier time, they notify the OR Clinical Director and we do our best to get them relieved.
What are the “strongest” subspecialties in your department?
Our strongest subspecialties are probably acute pain, regional anesthesia (approximately 3,700 peripheral nerve blocks/year), and intensive care (3,000 admissions/year). We also have strong pediatric, obstetric, and cardiac anesthesia experiences as well. We have the privilege of working with some especially strong surgical services, including otolaryngology, neurosurgery, orthopedic surgery, and general surgery (including transplant and trauma).
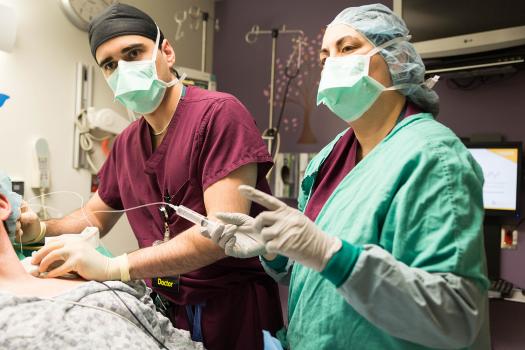
I've heard that you have a very strong regional anesthesia program. Is this true?
Absolutely true! We perform thousands of peripheral nerve blocks each year. Many of our faculty have expertise in regional anesthesia–including ultrasound guidance for blocks. Given these numbers, it shouldn't be surprising that our surgeons enthusiastically accept regional anesthesia as a beneficial part of patient care—something that cannot be said for every institution.
Residents rotate through the regional anesthesia service from CA-1 to CA-3 year and can request additional electives in regional anesthesia as well. Our graduates perform approximately 150 peripheral nerve blocks during their training.
What are your “weakest” rotations?
Our residents have no difficulties meeting their ACGME requirements in any area, so we really have no "weak" rotations. Like many other institutions, our cardiac surgical load (cases on bypass) is somewhat limited, but all residents are still able to meet their required case numbers and are more than prepared to go on to perform standard cardiac cases or pursue cardiac anesthesia fellowship. However, we do have a very popular senior cardiothoracic elective rotation in Des Moines for residents who would appreciate additional cardiothoracic experience.
Because Iowa City is such a pleasant and safe place to live, we do also see fewer penetrating trauma (gunshots, stab wounds, etc.) cases than some large city programs might see. However, we do have some cases come in from nearby communities, and we certainly see our fair share of blunt/penetrating trauma related to automobile accidents, farming equipment, and other unintentional traumas. As an institution that regularly performs high acuity cases and all types of transplants, we are more than equipped with the knowledge needed to provide care to acutely, critically ill patients. We truly appreciate the trauma experiences we are able to learn from while simultaneously living in such a safe, healthy community.
What electives do you have?
Away electives for seniors include:
Cardiothoracic anesthesia in Des Moines
International pediatric anesthesia in underserved foreign countries
UI Hospitals & Clinics anesthesia electives include:
All surgical subspecialties
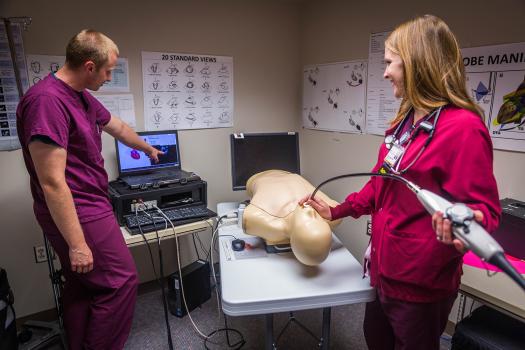
Simulation
ECHO
Ambulatory surgery anesthesia
Regional anesthesia
Advanced clinical anesthesia
Chronic pain
Research
Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
Do you offer international rotation experiences?
Yes, our CA3 residents have opportunities to participate, with our faculty, in mission trips to Guatemala and Colombia. We offer this opportunity to four to six of our CA3 residents and continue to explore opportunities for more residents to participate in these valuable international mission trips.