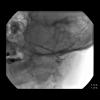
see also: Hypersalivation Ptyalism Sialorrhea; Botox injection to salivary glands for hypersalivation; Sialograms and Sialography; Botulinum neurotoxin infusion to the parotid via Stensen's duct Research protocol (IRB approved)
anatomy: Anatomy of Submandibular Gland and Duct; Bartholin's Duct anatomy; Buccal mucosa and Masticator space anatomy; Floor of Mouth Anatomy - Bartholin's Duct, Wharton's Duct, Sublingual Gland, Lingual Nerve, Uncinate Process; Relevant Anatomy for Sialendoscopy April 16 2015 Columbia Missouri; Submandibular Gland Anatomy: The Uncinate Process of the Deep Lobe; Submandibular Gland Anatomy: Vascular Supply - Ultrasound Imaging with Color Doppler; Surgical Anatomy & Physiology of Salivary Glands Lecture 2016
Anatomy
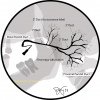
Parotid Gland
- Stensen's duct - Main parotid duct that opens into the parotid papilla
-
Iowa Salivary Duct Classification System (main duct, secondary ducts, tertiary ducts, acini)
-
1º (main duct): segment of duct from the oral cavity to the first major bifurcation
-
2º (secondary): segment of duct proximal to first major bifurcation and distal to second bifurcation
-
3º (tertiary): any duct proximal to the second bifurcation (including those that could be considered quaternary)
-
- Parotid papilla; parotid puncta - Small prominence or elevation onto which the Stenson's duct opens into the mouth. Found along the buccal mucosa adjacent to the 2nd molar
- Parotid orifice - True opening in which Stensen's duct opens into. Found within the parotid papilla/puncta
- Acini - Individual secretary unit in which saliva is formed.
- Serous Acini - Acini that secrete serous saliva that is rich in amylase (enzyme to help breakdown starch)
- Mucinous Acini - Acini that secrete mucinous saliva that is rich in the glycoprotein mucin and functions to lubricate the oral cavity that supports dental hygiene, antimicrobial activity, and swallowing.
- Adenomeres - Single unit of one or more acini joined with a single duct. (Grewal 2020).
- Lobules - Multiple adenomeres form a lobule. (Brazen 2021)
- Lobe - Multiple lobules, each separated by a connective tissue septum, form a lobe. (Brazen 2021)
Submandibular Gland
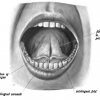
- Wharton's duct - Also known as submandibular duct; the main duct of the submandibular gland that drains into the floor of mouth through the sublingual caruncula (distinguish from "Warthin's tumor" see: Warthin's Tumor)
- Sublingual caruncula, caruncle, or sublingual papilla - Prominences on either side of the base of Lingual Frenulum representing the sites through which Wharton's duct drains.
- Lingual Frenulum - Band of connective tissue that is attached along the ventral tongue to the floor of mouth
- Plica- Derived from the Latin word plicare, to fold (Merriam-Webster online dictionary 2021)
- Plica Fimbriata - Derived from the Latin word, fimbria, meaning fringe; Plica Fimbriata are mucosal folds on the ventral side of the tongue running laterally on each side of the frenulum.
Sublingual Gland
- Bartholin's Duct - Common duct of sublingual gland that joins Wharton's duct to drain into the sublingual caruncle
- Ducts of Rivinus - Series of short ducts that drains saliva from the sublingual gland directly onto the floor of mouth
- Sublingual Fold or Plica Sublingualis - Elevated fold of mucosa along the floor of mouth indicating the sublingual gland through which the ducts of Rivinus drain
Salivation (see also Hypersalivation Ptyalism Sialorrhea)
- Sialorrhea or Hypersalivation - Excessive salivation (Merriam-Webster Online dictionary 2021)
- Ptyalism - Excessive flow of salivation
- Drooling - Unintentional loss of saliva from the mouth (Scully 2009)
- Gleek, Gleeking - Projection of saliva intentionally or non-intentionally
Dry Mouth
- Xerostomia (see also Management of Xerostomia) - Sensation of dry mouth due to decreased or absent saliva.
Common Salivary Pathologies
- Sialectasis (sialangiectasia) - Dilation or enlargement of salivary duct usually due to obstruction
- Sialolithiasis - Sialolith or salivary stones
- Sialadenitis (see also Salivary Swelling) - Inflammation of a salivary gland
- Sialosis (sialadenosis) - Chronic, non-inflammatory, non-neoplastic, diffuse swelling of major salivary glands, usually bilateral (Scully 2008)
References
Armstrong MA, Turturro MA. Salivary gland emergencies. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2013 May;31(2):481-99.
Brazen B, Dyer J. Histology, Salivary Glands. [Updated 2021 May 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551688/
Carlson GW. The salivary glands. Embryology, anatomy, and surgical applications. Surg Clin North Am. 2000 Feb;80(1):261-73, xii.
Ghannam MG, Singh P. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Salivary Glands. [Updated 2021 Jun 11]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538325/
Grewal JS, Bordoni B, Shah J, et al. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Sublingual Gland. [Updated 2021 Jul 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535426/
Holmberg KV, Hoffman MP. Anatomy, biogenesis and regeneration of salivary glands. Monogr Oral Sci. 2014;24:1-13. doi:10.1159/000358776
Scully C, Bagán JV, Eveson JW, Barnard N, Turner FM. Sialosis: 35 cases of persistent parotid swelling from two countries. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46(6):468-472. doi:10.1016/j.bjoms.2008.01.014
Scully C, Limeres J, Gleeson M, Tomás I, Diz P. Drooling. J Oral Pathol Med. 2009;38(4):321-327. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0714.2008.00727.x